Features
The characteristics and commands of POLYGONALmeister are explained below.
Characteristics
Explain the four features of POLYGONALmeister.
(1) Excellent for editing polygon data derived from measurement
(2) Manipulation of large-scale data is possible
(3) Edit a colored mesh
(4) Implemented with advanced geometric processing technology
Each feature is explained below.
(1) Excellent for editing polygon data derived from measurement
Compared to CAD-derived polygon data (mesh) , measurement-derived mesh has many irregularities such as self-intersections, and the smoothness of the surface is also inferior.
POLYGONALmeister has excellent editing ability even for meshes derived from measurement.
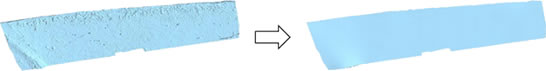
Automatic reshape
Repair the irregular part of the mesh derived from measurement, smooth the mesh, and reshape the faces to be close to equilateral triangles, just by clicking gExecuteh button .

Just one click!
Reduces wavy artifacts

Semi-automatic shape correction

(2) Manipulation of large-scale data is possible
As shown in the table below, POLYGONALmeister can operate a large amount of data compared to other commercially available SWs.
| Number of Polygons | 5 million | 12 million | 50 million | 190 million* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POLYGONAL meister |
5 sec. less than 1se. |
11 sec. less than 1sec. |
50 sec. few sec. |
ñ11ª 15 sec. |
| Software A | 14 sec. 1-2 sec. |
(lack of memory error) | - | - |
| Software B | 31 sec. 1-2 sec. |
70 sec. 1-2 sec. |
(not displayed after 90min.) | - |
| Software C | 24 sec. 1-2 sec. |
35 sec. 1-2 sec. |
(Data Unmeasured) | (not displayed after 60min.) |
| Software D | 33 sec. less than 1se. |
68 sec. 1-2 sec. |
80 min. not operable |
about 10 hours not operable |
Upper row: display time of reading. Lower row: rotation, zooming movement operation after reading.
Pcspecification: Intel Core i7, 3.5GHz, 32GBmemory. NVIDIA GeForce GTX680
[ * Data of 190 million faces used ]

Data provider: Fuji Technical Research
(3) Edit a colored mesh
POLYGONALmeister can edit the mesh without changing the color pattern (texture, face color, vertex color) attached to the mesh as much as possible.
The textured mesh on the left of the figure below consists of mesh shape information and image information

The textured mesh on the left of the figure below consists of mesh shape information and image information.
If you perform editing processes such as simplification in the same way as a non-textured mesh, the color pattern will be broken. POLYGONALmeister can be simplified without destroying the color pattern.

(4) Implemented with advanced geometric processing technology
Based on the cutting edge technology obtained through joint research with RIKEN, we are developing POLYGONALmeister using advanced geometric processing technology.
Preserves original shape features after simplification
In the figure below, the simplification results are compared between the POLYGONALmeister and two commercially available SWs.

A curved surface with no small irregularities is estimated from the mesh, and the vertices are moved on the surface to smooth the mesh. [Polish Smoothing]
Approximate a mesh to a smooth curved surface and divide the face into small pieces so that it fits on the curved surface. The mesh will be smooth. [Subdivision]
The specified area is reshaped into a flat or cylindrical surface. [Make Flat / Cylindrical]

Commands
The following describes some commands of POLYGONALmeister.
File Import / Export
The following files can be imported / exported.
The types of color in [ ] are supported.
STL files (ASCII or binary)
PLY files (ASCII or binary) [face color, vertex color]
OBJ files [texture, face color]
VRML files [texture, face color, vertex color]
OFF files
Edit
Cleaning
Inspect and correct the incorrect / defective parts of the mesh below.

Defeature
gDefeatureh removes through holes, blind holes, dents, protrusions, self-intersections, etc. in the specified area.

Smoothing
Smooth by removing the fine irregularities on the surface of the mesh derived from the measurement.

Simplify
Reduce the number of faces that compose the mesh.

Subdivision
The bulge of a face is estimated from the bending of the surrounding faces, and the face is divided so that it rides on the bulge.
This feature allows you to smooth the mesh when the face is rough and rugged.

Remesh
Reconstructs the mesh so that each face of the mesh is closer to an equilateral triangle.
There are two types of processing methods.

Cut
Cut the mesh using a swept surface of a straight line or a polygonal line.
It is possible to remove one of the cut pieces or leave both.

When there are multiple lines of intersection, it is possible to cut using only the selected lines.

Boolean Operation
Create union / difference / intersection of two shells.

Arrange Shells
Arrange shells according to various conditions.
Match two shells with similar shapes as closely as possible.

Move to match the 3 pairs of vertices.

Move so that the axis of cylinder A coincides with the axis of cylinder B.

Fill Caves
This function detects through holes and blind holes of a mesh and fills them.

Reshape Hole
Compensate for the irregularities in the round hole (through holes, blind holes, and holes in shells) to round.

Make Flat / Cylindrical
The specified area is reshaped into a flat or cylindrical surface.

Remove Protrusion
Detects and removes protrusions on the mesh.

Projection Solid
Sweep the open shell to a plane to create a solid shell.

Loop Cut
Cut with a free curve (polyline) in an inconspicuous place such as a color boundary

Data provided by: Mimaki Engineering Co., Ltd.
Reshape CT Mesh
Repair the irregular part of the mesh derived from CT measurement, smooth the mesh, and reshape the faces to be close to equilateral triangles.

Reshape Optical Mesh
Repair the irregular part of the mesh derived from CT measurement, fills small holes, smooth the mesh, and reshape the faces to be close to equilateral triangles.

Extension
Extend the mesh smoothly at the shell boundary.

Evaluation
Distance Contour
The difference between the two shapes is represented by a color map.

Example: Difference between before and after performing gReshape CT meshh
Data provided by RIKEN
Thickness Inspection
The color map of the mesh thickness is displayed.

Display Section Lines
Display intersections between the mesh and planes.

Find Path
Displays the shortest path (edge string) connecting two vertices.

Other evaluation functions
- Property
The following features related to the shape of the mesh are displayed.
- Surface area, Volume
- Center of gravity
- Size(Length of the range where the mesh exists in each coordinate axis direction.)
- Number of shells
- Number of shell boundaries
- Average / Maximum / Minimum edge length
- Distance
Measure the distance between two vertices.
- Coordinates
Display coordinate values.
- Circle Radius
Measure the diameter.
- Crease Detection
Detect edges that are bent more than the specified angle.
Color
Texture Alignment
Changes the area of the texture image referenced by the face.

Transfer Color
Pastes the mesh color of the external file into the (working) mesh as a texture.

Convert to Vertex Color
Change the "texture" or "face color" on the mesh to "vertex color".
This function is effective when the SW in the post-process cannot handle textures.

Data provided by: Mimaki Engineering Co., Ltd.
Segmentation
Divide the mesh into multiple color-coded areas based on shape feature.

Edit Segment Boundary
Merge segments that were divided by "Segmentation" command, and smooth a segment boundary.

Functions specialized in the field of use
Forming Arrangement
Arrange the mesh or shell on the forming table with a simple operation.
You can perform the placement operation while referring to the forming table.

Pinned Cut
Cut the mesh, and add protrusions and holes to the cut surface.(For assembling 3D printed objects)

Terrain Meshing
Read a geo information (GeoTIFF) file and create a mesh that reflects height information.

Soil / Space Volume
Displays the amount of soil or space volume (volume required to fill the soil) in the specified area.

Relief
Create an uneven mesh based on the image.

Embed Relief / Stamp
Adds an image or characters to the mesh as an uneven pattern.

Beta Functions
Wrapping
Create a new mesh using only the outside of the mesh.

Thicken
Add thickness to the shell.
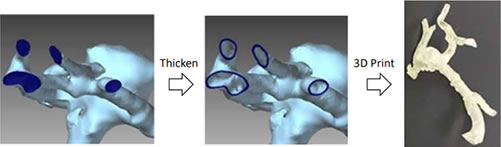
Application example: thicken the walls of blood vessels for 3D printing.
Sharpen
Makes a rounded ridge area into a sharp edge.



